Table of contents
- Introduction
- Benefits of Using Amazon S3 Storage Lens
- Exploring Use Cases for S3 Storage Lens
- Implementation Plan for Amazon S3 Storage Lens
- Best Practices
- Creation of S3 Storage Lens dashboard.
- Step1: Login to AWS Console and Navigate to AWS S3.
- Step2: Click on the Storage Lens section on the left pane then move to dashboards.
- Step3: Dashboard Creation
- Step4: Provide details for Dashboard
- Step5: Select Regions and Buckets
- Step6: Metrics Selection for the dashboard
- Step7: Metrics Export
- Step8: Select Create dashboard.
- Step9: Navigate to AWS S3 Storage Lens Dashboard
- Little more about Advance Metrics:
- Disabling of S3 Storage Lens Dashboard
- Deletion of S3 Storage Lens Dashboard
- Conclusion
Introduction
Tired of reading through reports and notifications to get the insight about the S3?
Well dashboards are a greater way to understand the above in more practical and comparable way. Amazon S3 Storage Lens is an ultimate tool which offers data usage and access pattern insights of the AWSS3 storage. It helps organizations in a lot many ways apart from cost optimization, Here are some ways use Amazon S3 Storage lens dashboard- to optimize costs, boost performance, and improve and e data management strategies. Here we will explore the key features, benefits, and effective implementation plans for using S3 Storage Lens.
Features of Amazon S3 Storage Lens
Availability of Comprehensive Metrics:
One of the Metrics based upon the Total storage usage, number of objects and distribution across multiple storage classes, we can call this as Storage Metrics
Other being differentiated based on the insights into the patterns and frequency of access of data, named as Access Metrics
Dashboards Visualizations:
- The dashboards are better way to represent the metrics, trends and historical data for the analysis and forecast.
Provides Insights for Optimization:
- S3 Storage lens provide us recommendations for optimizing the storage cost depending on how we are accessing the data i.e.., Access pattern. It also includes suggestions for transitioning the data to different storage classes to save more cost.
Actively Monitoring of the data for cost savings:
- With Amazon S3 Storage lens, usage patterns and access can be monitored to identify the most frequently access data and the infrequently used/orphan data which can be cleaned up to save on unnecessary cost.
Seamless Integration with other AWS Services:
- With this feature in S3, other services like CloudWatch, CloudTrail etc, can be seamlessly integrated for enhanced monitoring
‘N’ Number of Custom Metrics and Filtering:
- Within dashboard there can be a number of permutation-combinations when it comes to filter data & metrics based on the specific criteria for self analysis or project requirements.
Benefits of Using Amazon S3 Storage Lens
Cost Optimization: Evaluate the infrequently accessed data which can be further moved to appropriate storage classes or can be cleaned up.
Improved Data Management: With the evaluation on how data is being used or accessed, it can be move to appropriate storage class via lifecycle management.
Enhanced Security and Compliance: Usage patterns and access can be monitored to make sure the compliance requirement and Data management policy aligns with one another.
Informed Decision-Making: The analytics and trends is comprehensive which is useful to make informed decisions based.
Exploring Use Cases for S3 Storage Lens
If you are still clueless on how to begin, here are few use cases which you can simply start configuring in no time and get some money saved 💵💰
Use Case 1: Identifying the huge, Unmonitored Buckets
The Challenge
You have ‘n’ number of bucket and it is always tiring to check them one by one to understand if the data stored in them is still relevant or outdated, when they were last accessed, what is the size of bucket and which among them is the largest?
Some of them might contain valuable data, while others may no longer serves the purpose. However, without a systematic approach to monitor these buckets, organizations are overspending and over splurging on storage costs because let’s be honest “DATA IS EVERYTHING“
The Solution with S3 Storage Lens
With S3 Storage Lens we can get the overview of bucket size and activity trends on it. Now how to find out: “Which Bucket has the largest size out of all“?
By utilizing this tool, one can easily identify large buckets that may be unmonitored. Here’s how to effectively use S3 Storage Lens to tackle this challenge:
Access the S3 Storage lens Dashboard: Start by navigating to the S3 Storage Lens dashboard in the S3 Console. The dashboard gives a high-level overview of your storage metrics, also bucket sizes.
Filter for Size Metrics: Use the filter option to segregate based on "Size" metrics. This will let you to quickly pinpoint the buckets with most storage space.
Analyze the Historical Trends: Analyze the historical data visible for the past 14 days. This will lead to the understanding that how bucket size has been increased/decreased over time.
Identify Unmonitored Buckets: Once you identify the largest buckets, check and run the same through organizational data management policies. This will help you identify any unmonitored/unused buckets.
Action on it: After identifying these buckets, you can decide for further steps—whether it required to be archived, cleanup data, or migrating data to a more cost-effective storage solution via lifecycle policies.
Real-World Example
Consider a for a campaign, digital marketing agency has stored data in multiple S3 buckets. Over time, multiple buckets has been created for different clients, but as projects ends, some buckets remained untouched. By using the Amazon S3 Storage Lens, the agency listed a few large, unmonitored buckets that has old/outdated campaign data which is no longer required. So, they proceeded with deleting these files/data and cleaned up buckets, which significantly lowered their storage costs.
Use Case 2: Optimizing the overall Cost by Using AWS S3 Storage Classes
The Challenge
Storage costs quickly spikes if data is not stored or managed properly. Many organizations use standard S3 storage class for all their data, without analyzing its access patterns. Unknowingly leads to huge bills especially for the rarely accessed or archived data.
The Solution with S3 Storage Lens
S3 Storage Lens provides insights on how their data is being accessed and provide suggestions to move them to the most suitable S3 storage classes. Here’s how you can do it too:
Review Access Patterns Initially: Firstly proceed by analyzing the access metrics available in AWS S3 Storage Lens. Now filter out the trends indicating the frequently/infrequently accessed data
Categorize the Data based on access pattern: Based on access patterns, divide your data into multiple different groups. Example: shortlist frequently accessed data (hot data) from the infrequently/rarely accessed (cold data).
Evaluate Storage Class Options for the categorized data: Once your data is categorized, evaluate the various S3 storage classes available, such as:
S3 Standard: For frequently accessed data, which is required within no time.
S3 Intelligent-Tiering: For unpredictable access patterns, use this option.
S3 Standard-IA (Infrequent Access): For data that requires quick access when needed but is less frequently or infrequently accessed.
S3 Glacier: If you don’t worry for the longer retrieval times then archiving data is the best suited option.
Implement Transitions for storage class using Lifecycle policies: Use lifecycle policies for the transition of data between different storage classes based on its access patterns automatically as mentioned in previous point.
Regularly Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor the storage costs, usage and access patterns through the S3 Storage Lens dashboard. Adjust the lifecycle policies as required to ensure the costs effectively.
Real-World Example
A banking firm uses S3 Standard for all their data, including huge volumes of older financial records. By analyzing the access patterns through S3 Storage Lens, they came to the conclusion that most of their data hadn’t been accessed in long time still is stored in Standard class which is costing them fortune. They transitioned this data to AWS S3 Glacier, which drastically lowered their storage costs without compromising data availability.
Use Case 3: Finding Buckets That Are No Longer Accessed
The Challenge
While Project is new and we are configuring the S3 Bucket for data storage, its easier to create multiple buckets which we lost track of in longer duration. They are rarely or never accessed, and costing fortune with a security risk for the outdated data.
The Solution with S3 Storage Lens
S3 Storage Lens help to find the neglected buckets, allowing better data governance and cost management. Here’s how you can do it too:
Utilize the Access Metrics section: Filter the access metrics to determine the buckets which have not been accessed over a significant long period.
Identify the Inactive Buckets: Search for buckets with zero or no access over a longer timeframe like last 30 or 90 days. This means either it is no longer needed or should be reviewed for transition.
Evaluate the data: For inactive buckets , analyze the data in it. Evaluate if it can be archived or deleted.
Configure data Retention policy: Configure Data retention policies that define how these long different types of data should be kept and when it should be reviewed or deleted.
Cleanup inactive or transition them: Based on the final assessment, decide whether to keep, delete inactive data or archive for cost effectiveness.
Real-World Example
A leading Educational organization had multiple S3 buckets that were created for specific Years, but as projects ended, the data in those buckets went unmonitored. With S3 Storage Lens, they concluded that multiple buckets that hadn’t been touched in over an year now. After reviewing the data, they found that most of the data were trivial and could be cleaned up, resulted in huge cost savings and their data governance and management.
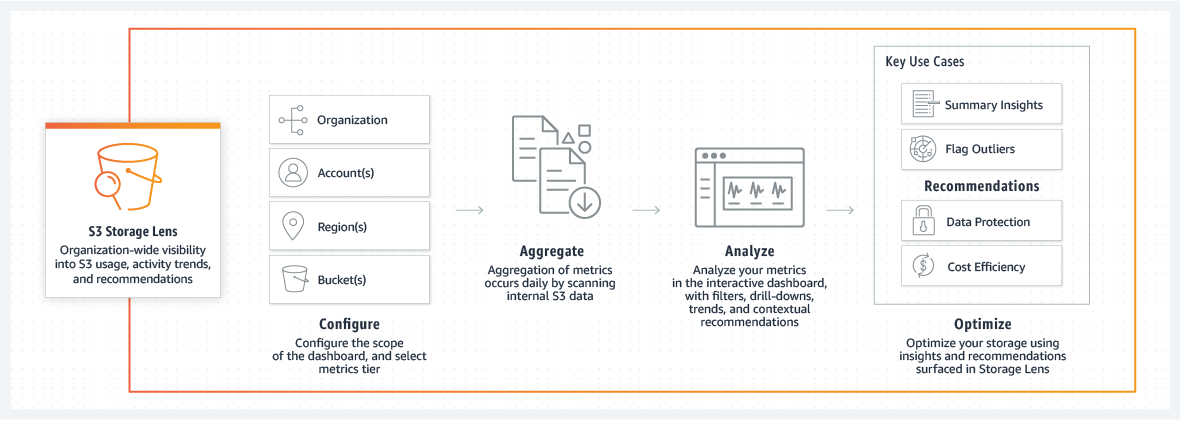
Implementation Plan for Amazon S3 Storage Lens
This is just the overview, there is detailed section below on “How to create S3 Storage Lens Dashboard“
Step 1: Enabling Storage Lens first
Start with logging in to your AWS account and navigate to the Amazon S3 console.
On the left pane, click on "Storage" then “Storage Lens“.
Now, click on “Create dashboard” and provide a valid name(which should follow the naming convention) and description for your dashboard accordingly.
Choose the metrics that you want to include (e.g., total storage, number of objects, etc) and apply the filters to target the desired buckets or prefixes.
Choose the reporting frequency like daily, weekly, or monthly followed by the location where you want it to be stored (e.g., S3 bucket).
Review the configurations once again to ensure everything is properly added then click “Create dashboard.”
Step 2: Analyze Metrics
For analyzing, navigate to the newly created dashboard to view the metrics and visualizations.
Analyze the data to understand the trends in storage usage, access patterns, and fetch the potential areas for optimization.
Step 3: Optimize Storage
Check the optimization insights that you got in above steps by Storage Lens to identify the cost-saving opportunities.
Move data to more appropriate storage classes based on the access and usage patterns. (Like from S3 Standard to S3 Infrequent Access or S3 Glacier depending on the frequency of data being accessed)
Step 4: Monitor and Adjust
Regularly review the Storage Lens dashboard to be updated on usage trends, metrics and cost-optimization opportunities.
Modify the metrics, filters, and reporting settings according to the business needs or storage data usage patterns.
Step 5: Integrate with Other AWS Services
Integrate S3 Storage Lens with AWS CloudTrail by setting up AWS CloudTrail to monitor the API calls made on your specific S3 buckets for enhanced security and compliance.
Integrate S3 Storage Lens with AWS CloudWatch by creating CloudWatch alarms based on the S3 Storage Lens metrics to receive notifications for significant specific changes in storage usage or access patterns.
Best Practices
Small Steps: Begin with a few smaller buckets to understand how it works and how it can be helpful in understanding the patterns before scaling to all your resources.
Monitor Regularly: Regular monitoring and altering the settings based on usage patterns to meet the organizational requirements.
Learn first then Educate Team Members: Make sure that the relevant team members understands on how to access and interpret the dashboards and Storage Lens data.
Creation of S3 Storage Lens dashboard.
In the above section we have seen all the steps, Let’s dive deeper and implement it to create our first S3 Storage lens Dashboard.
Step1: Login to AWS Console and Navigate to AWS S3.

Step2: Click on the Storage Lens section on the left pane then move to dashboards.

Step3: Dashboard Creation
By default there will be no dashboards in any regions of your account. For the creation of new dashboard, click on “Create Dashboard”

Step4: Provide details for Dashboard
- Dashboard Name: This must be <65 character and should not contains any special characters & spaces.
Status: This shows the status of the dashboard to display metrics:
Disable: meaning no display metrics for dashboard
Enable: meaning to display updated daily metrics
Tags: This is optional, you can add tags for the dashboard depending upon permission or for cost allocation in case of Advance metrics selection.

Step5: Select Regions and Buckets
5.1: When all the Regions and Buckets are Selected:
- The dashboard created after selecting this option will include all of the regions and all the buckets for the selected account.

5.2: When you want to exclude Regions and Buckets:
The dashboard created after selecting this option can exclude some of the regions and some buckets for the selected account.
You can provide the region and bucket name which you want to exclude in the dashboard.

Step6: Metrics Selection for the dashboard

6.1: While selecting Free Metrics:
Free metrics will be available once dashboard is created, these metrics are relevant to your storage usage.
Includes usage metrics collected at the bucket level. Data is available for queries for 14 days only by default.
Free metrics include use-case-based metrics like below:


6.2: While selecting Advance options:
Apart from the free metrics still you required to enable the advance metrics there are additional charges.
In Advanced metrics data is available for queries for 15 months which is very helpful for the analysis for longer duration.
This include metrics like advanced data-protection and cost-optimization along with the free metrics.



Step7: Metrics Export
The data in this dashboard can be moved to S3 bucket, which can be further used for analyzing or forecasting.
Disable: By default Metrics export will be disabled, meaning data from the dashboard will not be exported to S3 destination.

Enable: If it is enabled, then there is an option to select the output format accordingly with which the data from the dashboard will be stored in S3 destination, including Server side encryption. This option will export data to a specified AWS S3 bucket in every 24 hours. It is not enabled by default, we have to enable it according to the requirement


Step8: Select Create dashboard.

Step9: Navigate to AWS S3 Storage Lens Dashboard
9.1: Once the dashboard is created, it may take ~24-48 hours to generate initial metrics, click on them to get more details:
Filters: You can filter the data in dashboard depending upon multiple filters like: Accounts, AWS Regions, Storage classes, Buckets, Storage Lens groups and Prefixes.
Overview: This shows the trend for all of the metrics with details.

9.2: The next section shows trend line for each metrics over last 30days and % change(for advance metrics selection) in terms of day but can be modified to week or month.

- The metrics categories in drop down has more selections as well like: Activity, Access management, Cost optimization, Data protection, Events, Summary, and Performance.
9.3: For plotting the Trends and Distributions, here two metrics: Primary and secondary can be used for the comparison.
Here I have selected (you can go ahead with other metrics too):
Primary Metrics: Total Storage
Secondary Metrics: Object Count

9.4: Below shows how the above selected two metrics are distributed across different Storage Class Distribution and AWS Regions Distribution.

9.5: Last section gives overview to perform analysis for Top N (1<=N<=25) metrics selected over desired date range. You can also choose Day/Week/Month for better comparison

Little more about Advance Metrics:
Upgrading provides you flexibility to access to 35 additional metrics along with 15 months of historical data. These metrics is helpful in fetching the insights of storage activity like request counts, data protection(by utilizing S3 Replication), cost optimization(by S3 Lifecycle management).
With the seamless integration of other AWS services like Amazon CloudWatch alarms can be configured based on requirement and metrics can be sent via API. This adds up in making the AWS environment more optimized and enhance performance.
Automated recommendations is available with relevant metrics in the dashboard based on the current usage which can be actioned
You’ll see three main types of recommendations:
Suggestions: This highlight trends point to the opportunities cost savings or improving your data protection practices.
Call-outs: This is like alarm, in case any unusual/suspicious activity takes place in your storage that might need a check.
Reminders: This is to keep reminding us on how to use the features effectively for low costs and maintaining data security.
Disabling of S3 Storage Lens Dashboard
Disabling will no longer receive any new daily metrics. But yes until the dashboard is not deleted, it can be re-enabled within the expiration period to access the historical data.
Historical data is available for 14 days and post that is expired in case of Free metrics.
While for Advance metrics, the expiration period will be 15 months.
Deletion of S3 Storage Lens Dashboard
Deletion is permanent and can’t be reversed or re-enable once done.
Once dashboard is deleted, all the associated historical data will be lost and the dashboard will no longer receive new metrics.
In case the dashboard needs to be restored or want to access the historic data for the deleted dashboard, new dashboard needs to be created with same name in the same Region.
Conclusion
S3 Storage Lens is a ultimate tool for optimizing Amazon S3 storage. It helps in identify the most frequently access data and the infrequently used/orphan data which can be cleaned up to save on unnecessary cost.
By leveraging these insights, the data management can be streamlined, cost efficiency and optimization can be improved. This feature provides us visibility to make decisions based on the analysis using multiple metrics and filters to boost the overall performance
Happy Learning!!